Conquering Chronic Conditions: Expert Tips and Exercise Solutions (Updated Oct 2024)
⇒ Introduction:
Keeping fit in today’s fast world is not something you can just be born fit and is an uphill task. Not only are there chronic conditions – which include diabetes, hypertension and chronic back pain – but the conditions are manageable or even preventable with some informed intervention. In this article, we will look into these three health issues in depth and take a look at their causes, symptoms, preventions strategies and even specific exercises that help alleviate and manage these conditions. We also explore the most recent research and advances in these fields.
⇒ Disease/Condition 1: Diabetes

1.Definition and Types:
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body struggles to regulate blood sugar. The most common types are:
Type 1 diabetes:

An autoimmune disease where the pancreas produces little to no insulin.
Type 2 diabetes:
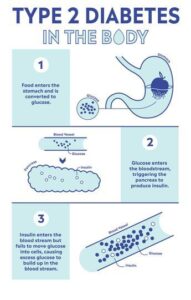
Often associated with obesity and lifestyle, this form results from insulin resistance.
Gestational diabetes:

Occurs during pregnancy and can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later.
2.Causes:
Genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet are leading causes of diabetes, especially Type 2.
Environmental factors and autoimmune responses contribute to Type 1 diabetes.
3.Symptoms:
Common symptoms includes following:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision.
4.Prevention Strategies:
Healthy diet: Prioritize low-glycemic foods, such as vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
5.Regular exercise:

Helps improve insulin sensitivity.
Weight management: Losing as little as 5-10% of body weight can prevent or delay Type 2 diabetes.
6.Exercise Solutions:
Aerobic exercises:
Brisk walking or swimming for at least 150 minutes weekly.
Resistance training:
Exercises like weightlifting or bodyweight movements (e.g., squats) twice a week.
Flexibility exercises:
Include yoga or simple stretching to improve overall function.
7. Latest Research (October 2024):
Today, AI-driven personalized nutrition programs are offering tailored meal plans as a tool to control diabetes, and the newest research demonstrates that AI-driven meal planning can lower HbA1c levels by 15 percent in just six months.
⇒ Disease/Condition 2: Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)

1. Definition and Stages:
Hypertension is a condition characterized by consistently elevated blood pressure, with readings over 130/80 mm Hg. It is classified into:
Mild (Stage 1): 130-139/80-89 mm Hg.
Moderate (Stage 2): 140/90 mm Hg or higher.
Severe: Over 180/120 mm Hg, requiring urgent intervention.
2.Cause:
Contributing factors include;
- Family history.
- High salt intake.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
3.Symptoms:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Sometimes chest pain is a common symptoms, but many cases are asymptomatic.
4.Prevention Strategies:
Diet:
A diet low in sodium and high in potassium–rich foods such as fruits and vegetables are key.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity like brisk walking or cycling helps regulate blood pressure.
Stress management:
Mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing exercises help reduce stress-related hypertension.
5.Exercise Solutions:
• Cardiovascular exercises:
Jogging, swimming, or brisk walking for at least 150 minutes a week helps lower blood pressure.
• Strength training:
Incorporating resistance bands or bodyweight exercises can enhance overall cardiovascular health.
• Relaxation techniques:
Practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises to lower stress levels.
6. Recent Guidelines (2024)
New research shows that exercise alone can reduce systolic pressure by 5-10 mm Hg and so the American Heart Association (AHA) now recommends that people at risk of hypertension have 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week.
⇒ Disease/Condition 3: Chronic Back Pain
1. Definition and Types:
Chronic back pain is defined as persistent pain lasting more than three months. The main types are:
Lower back pain:
The most common form, often caused by muscle strain or herniated discs.
Upper back pain:
Generally related to poor posture or musculoskeletal issues.
Sciatica:
Pain radiating along the sciatic nerve from the lower back down the leg.
2.Causes:
Factors include poor posture, repetitive strain, herniated discs, and muscle imbalances.
3.Symptoms:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Muscle spasms
- Limited mobility are typical symptoms.
Nerve involvement can lead to numbness or tingling sensations.
4.Prevention Strategies:
Ergonomic adjustments:
Proper desk setup, chairs, and monitor heights can alleviate strain.
Exercise:
Regularly strengthening and stretching muscles, particularly in the core, helps prevent pain.
5.Exercise Solutions:
Stretching exercises:
Focus on hamstrings, hip flexors, and the lower back.
Strengthening exercises:
Engage the core and lower back muscles through exercises like planks and bridges.
Flexibility exercises:
Yoga and Pilates are ideal for improving flexibility and preventing back injuries.
6. Breakthrough Research (2024)
Lessons of recent advances in spinal cord stimulation (SCS) have promised to boost patients suffering chronic lower back pain by precisely targeting nerves that transmit pain signals.
⇒ Common Exercise Solutions:
1. Benefits of Exercise:
Exercise not only prevents but also controls chronic conditions. Physical activity decreases the likelihood of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and musculoskeletal disorders.
2. Sample Workout Routines:
For diabetes:
a mix of aerobic and resistance training is effective.
Hypertension:
benefits from a balance of cardiovascular and relaxation exercises.
For chronic back pain:
low-impact aerobic exercises and core strengthening are recommended.
3. Tips for Incorporating Exercise into Daily Life;
Set short-term goals:
Start with small daily targets, like walking for 15 minutes.
Break it up:
Fit exercise into your schedule with short sessions throughout the day.
Stay consistent:
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
⇒ Conclusion:
However, chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and chronic back pain are all prevalent but manageable by a combination of lifestyle changes, exercise, and the latest in technological advances. These articles will teach people how to follow the prevention strategies and exercise solutions outlined in this article, allowing them to take their health into their own hands, prevent complications, and improve the quality of their lives.
⇒ FAQs:
- What is the most common type of diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common, accounting for over 90% of all cases. - Can hypertension be cured?
Hypertension can’t be cured but can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication. - How often should I exercise if I have back pain?
Experts recommend low-impact aerobic exercises 3-5 times per week for those with chronic back pain. - What are the best foods for managing diabetes?
Low-glycemic foods like whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins are highly effective. - What is the average recovery time for back pain?
Recovery time varies, but most patients recover within 6–12 weeks with the right interventions. - Is AI playing a role in diabetes management?
Yes, AI is increasingly used for personalized nutrition and glucose monitoring systems. - What exercises can help reduce blood pressure?
Cardio and strength training exercises are the most beneficial. - Are there any new treatments for chronic back pain?
Spinal cord stimulation is an emerging treatment, offering relief for severe cases. - How does resistance training help with diabetes?
It improves insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, helping to manage blood sugar levels. - Is chronic back pain permanent?
Not necessarily. With proper treatment, most cases can be significantly improved or resolved.
Note:
If you have any questions, then comment on post we will respond as soon as possible.
thank you all to visit our site to get new tips and increase your knowledge. To get new blogs, visit our site daily.
share this to your friends: www.know-tips.com



